![]()
Astronomers derive distances to the nearest stars (closer than about 100 light-years) by a method called stellar parallax. This method that relies on no assumptions other than the geometry of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. You are probably familiar with the phenomenon known as parallax. Try this. Hold out your thumb at arm's length, close one of your eyes, and examine the relative position of your thumb against other distant (background) objects, such as a window, wall, or tree. Now look at your thumb with your other eye. What do you notice? Move your thumb closer to your face and repeat the experiment. What was different this time? This is a demonstration of the parallax effect: the apparent shift in position of a relatively nearby object against more distant ones when viewed from different vantage points.
Now consider that the Earth moves in its orbit around the Sun, allowing us to look at nearby stars from slightly different locations - just like your two eyes are at slightly different locations. This is shown in the image below.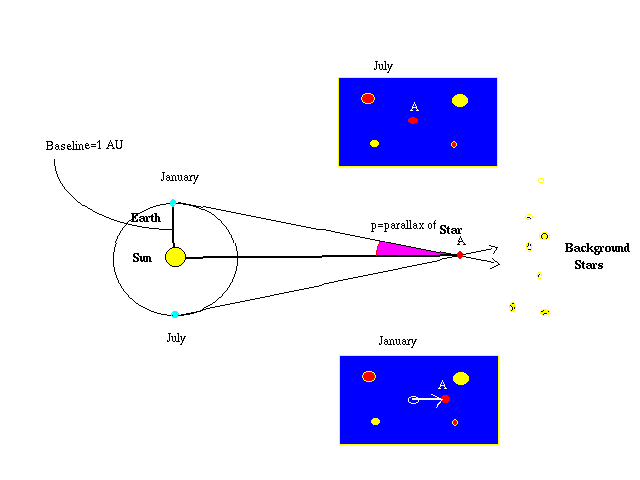
From the image above, you can see that by knowing the size of Earth's orbit and measuring the angles of the light from the star at two points in the orbit, the distance to the star can be derived. The farther the star is, the smaller the angles. For stars more than about 100 light-years from Earth, we cannot measure any shift and the method fails.
The mathematical formula of a parallax distance is:
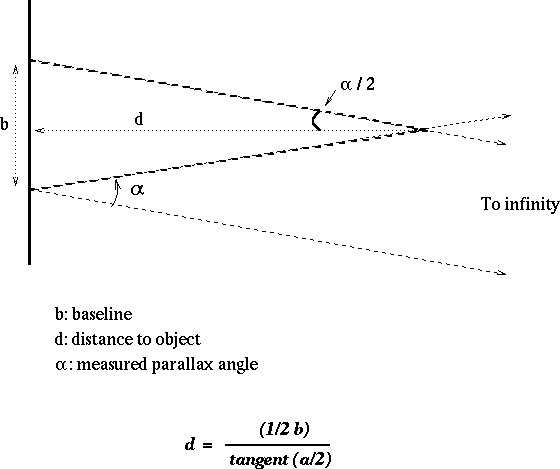
![]()
The StarChild site is a service of the High Energy Astrophysics Science Archive Research Center (HEASARC), within the Astrophysics Science Division (ASD) at NASA/ GSFC.
StarChild Authors: The StarChild Team
StarChild Graphics & Music: Acknowledgments
StarChild Project Leader: Dr. Laura A.
Whitlock
Curator:
Responsible NASA Official: